English small Alphabets Letter a to z Free Printable worksheet for kids.
These Worksheet aim to keeping your kid practicing even though they are at home.
These worksheets are suitable for preschool kindergarten, nursery kids.
You can easily download all worksheet in Pdf A4 format.
1- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘a’ Tracing Worksheet
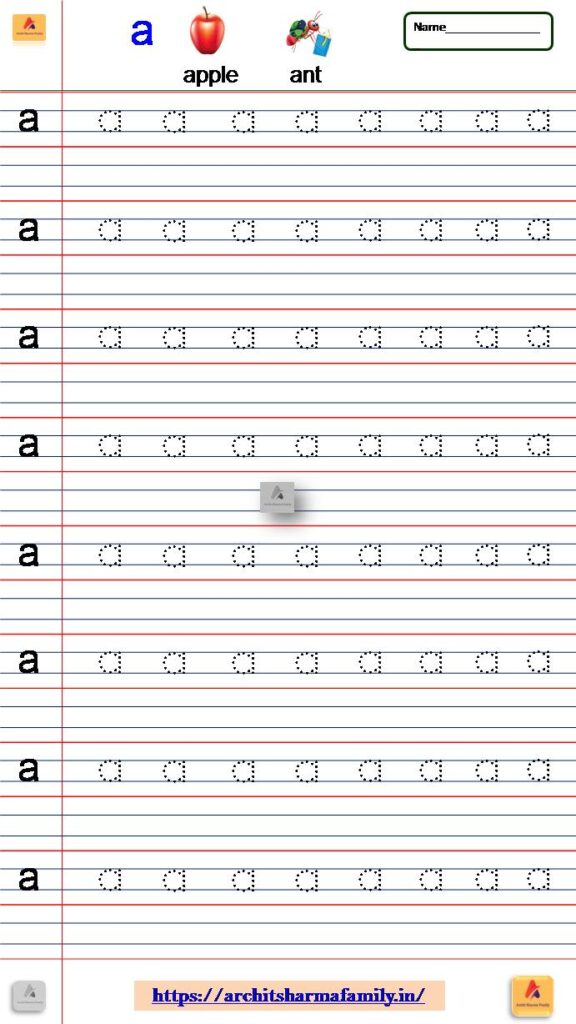
Download Small Letter a tracing Worksheet
2- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘b’ Tracing Worksheet
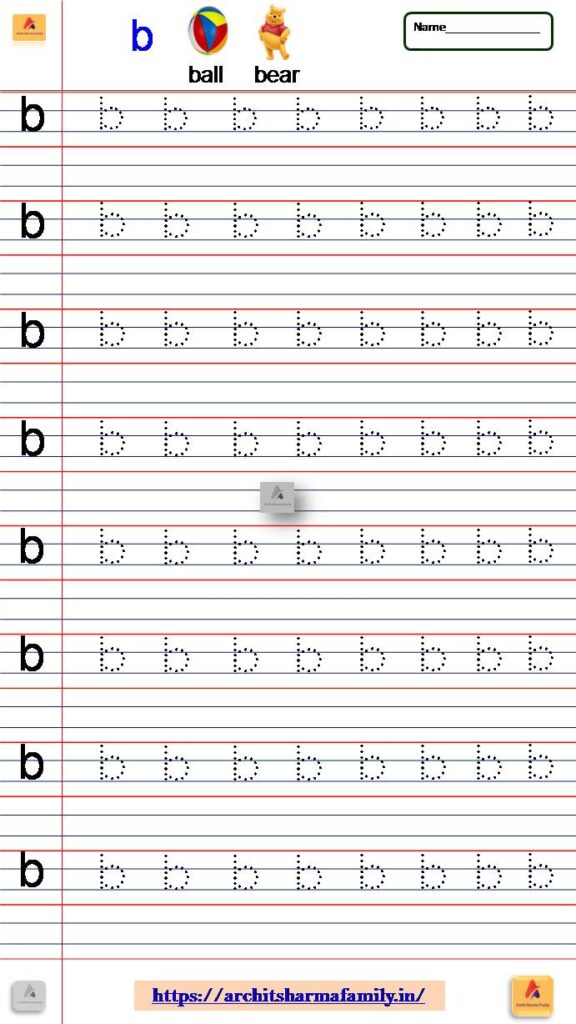
Download Small Letter b tracing Worksheet
3- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘c’ Tracing Worksheet
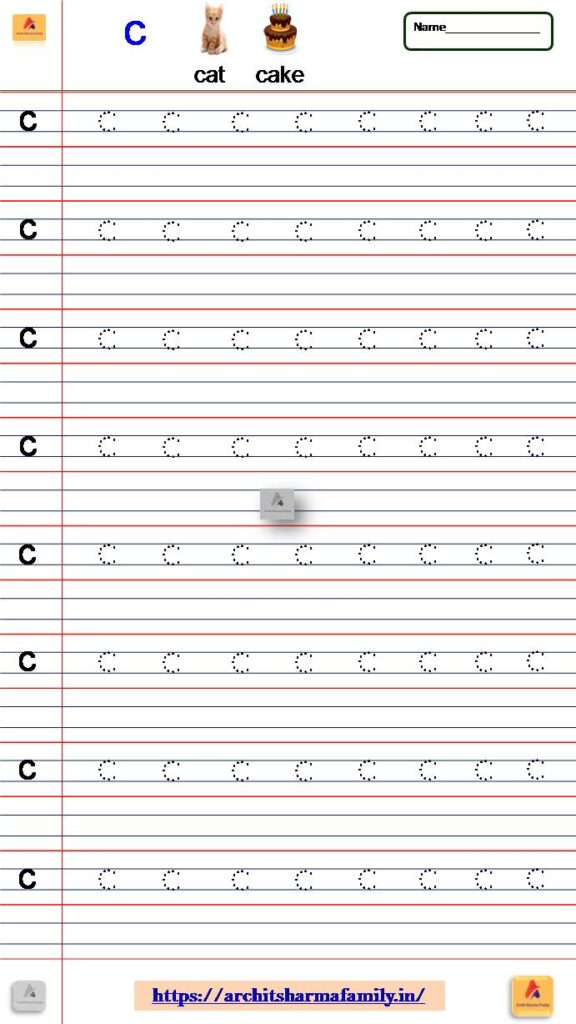

Download Small Letter c tracing Worksheet
4- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘d’ Tracing Worksheet

Download Small Letter d tracing Worksheet
5- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘e’ Tracing Worksheet
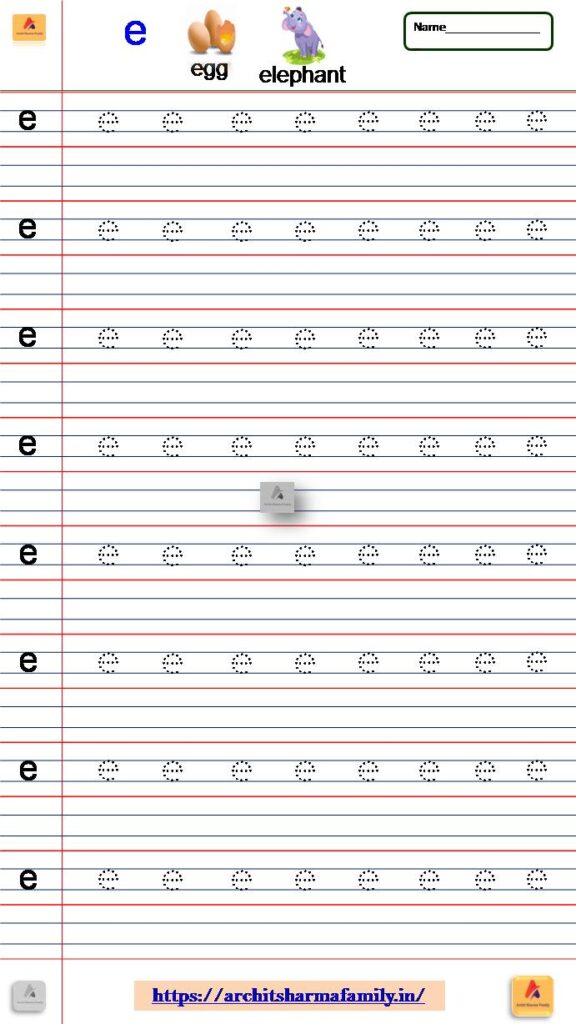
Download Small Letter e tracing Worksheet
6- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘f’ Tracing Worksheet
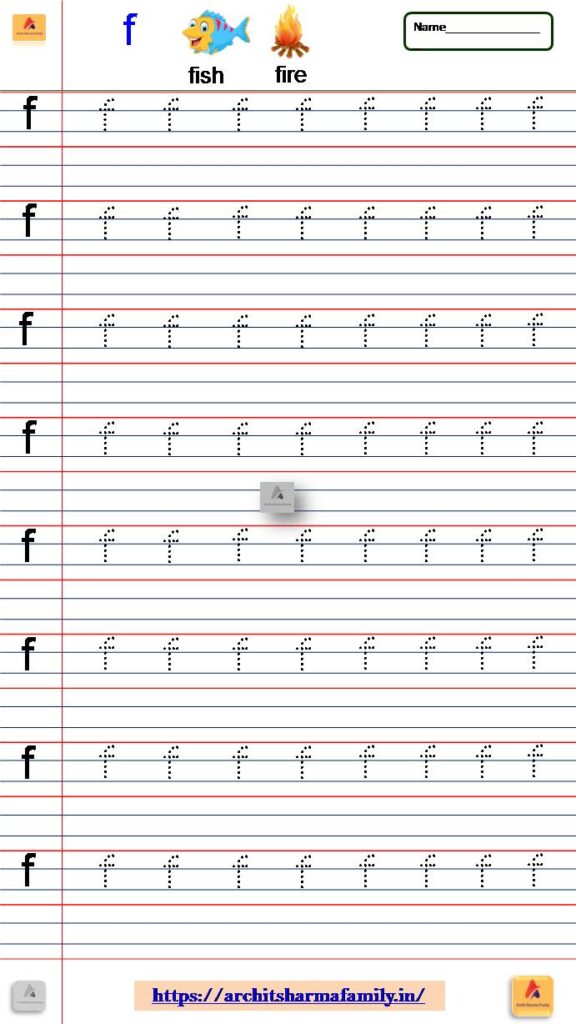
Download Small Letter f tracing Worksheet
7- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘g’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter g tracing Worksheet
8- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘h’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter h tracing Worksheet
9- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘i’ Tracing Worksheet
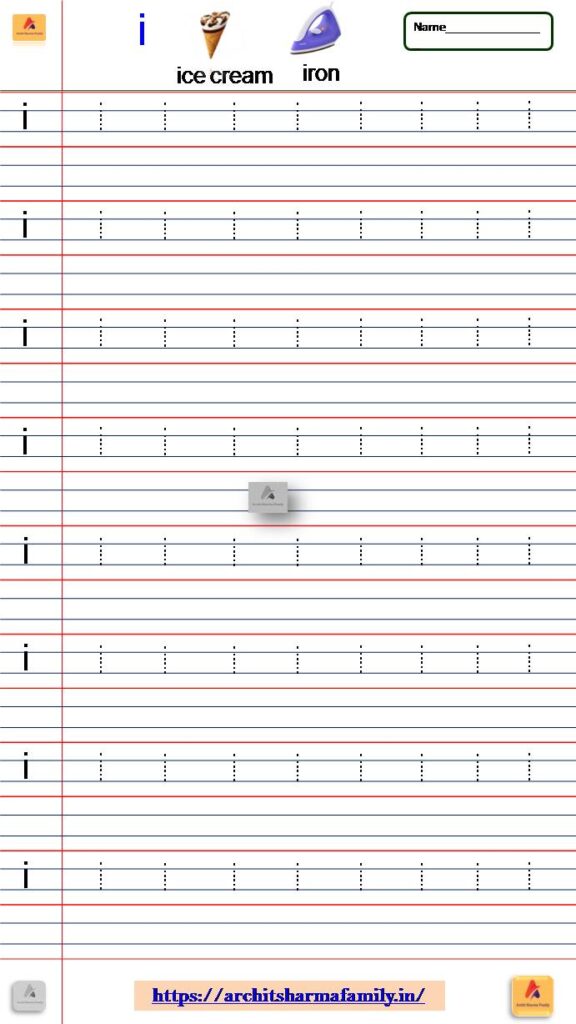

Download Small Letter i tracing Worksheet
10- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘j’ Tracing Worksheet

Download Small Letter j tracing Worksheet
11- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘k’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter k tracing Worksheet
12- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘l’ Tracing Worksheet

Download Small Letter l tracing Worksheet
13- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘m’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter m tracing Worksheet
14- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘n’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter n tracing Worksheet
15- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘o’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter o tracing Worksheet
16- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘p’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter p tracing Worksheet
17- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘q’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter q tracing Worksheet
18- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘r’ Tracing Worksheet

Download Small Letter r tracing Worksheet
19- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘s’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter s tracing Worksheet
20- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘t’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter t tracing Worksheet
21- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘u’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter u tracing Worksheet
22- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘v’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter v tracing Worksheet
23- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘w’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter w tracing Worksheet
24- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘x’ Tracing Worksheet
Download Small Letter x tracing Worksheet
25- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘y’ Tracing Worksheet

Download Small Letter y tracing Worksheet
26- Lowercase Letter (small letter) ‘z’ Tracing Worksheet


centrifuge balancing
When discussing the critical aspect of centrifuge balancing, it is essential to realize its profound importance in various industrial operations. Centrifuges serve as vital components within sectors such as chemical processing, food production, oil and gas extraction, and pharmaceuticals. Their ability to operate at high speeds while maintaining a balanced state is crucial for efficiency and product quality. Without proper centrifuge balancing, industries can encounter severe consequences, ranging from machinery failure to the degradation of end products.
The impact of imbalance within a centrifuge cannot be overstated. It poses risks such as decreased product quality and increased operational waste. For instance, in the food industry, an unstable centrifuge can lead to the spoiling of numerous product batches, ultimately resulting in significant financial losses. Moreover, a lack of effective balancing can cause accelerated wear on critical components like bearings and shafts, leading to the untimely breakdown of machinery. I have witnessed firsthand how poor balancing decisions can halt entire production lines due to equipment failure.
Imbalances also lead to excessive noise levels caused by strong vibrations, creating a challenging work environment that could affect employee health and safety. Other potential risks include uneven loads that may result in cracks in the centrifuge casing or the loosening of crucial components. The importance of addressing these issues is clear, as even small imbalances can snowball into considerable disasters if left unchecked.
Dynamic centrifuge balancing is particularly crucial given the potential consequences of operating machinery without proper balance. As rotation speeds increase, so do the risks. I recall attending a facility where neglecting balancing resulted in the catastrophic failure of a costly centrifuge. Such incidents highlight why regular condition assessments and timely balancing interventions are necessary. Not only do they extend the equipment’s lifespan, but they also prevent costly downtime and operational interruptions.
Performing dynamic balancing directly at the installation site is regarded as the most effective approach to maintaining centrifuge stability. This method utilizes the existing support bearings of the machine, which provides several advantages. First, it allows for rapid execution without the delays associated with transportation and disassembly of equipment. I remember a situation where this approach saved an entire day of production.
Accuracy is another significant benefit of on-site dynamic balancing, as it minimizes the risk of distortions that can occur when components are balanced outside of their operating conditions. This technique reduces the likelihood of experiencing minor but persistent issues that could result in long-term complications. Additionally, dynamic balancing reduces the need for complex assembly and disassembly processes, saving valuable time and resources for operations.
To achieve optimal results, dynamic balancing aims for the lowest possible residual imbalance, ensuring that the centrifuge operates flawlessly post-procedure. I have encountered instances where proper balancing transformed equipment performance, allowing it to function as if it were brand new.
The Balanset-1A vibration analyzer serves as a key tool in the balancing procedures. With its precision and ease of use, it stands out as a vital device for assessing vibration levels and guiding the balancing process. For effective balancing of a centrifuge rotor, a series of methodical steps must be followed. These include the setup of vibration sensors, installation of a tachometer, and connection of all devices to the Balanset-1A.
The initial measurements are crucial to understanding the baseline vibration levels of the centrifuge. Following the preparation of the equipment, the first balancing phase begins by adding a test weight in the first measurement plane. After conducting these measurements, the same process continues with a second plane for accuracy. Following the program’s guidance on weight adjustment ensures that the balancing process aligns with the optimal operating condition of the centrifuge.
In every instance of balancing, adhering to established standards, such as ISO 1940-1-2007, is crucial. These standards outline acceptable vibration levels for various classes of machinery, ensuring that adherence leads to efficient, reliable centrifuge operation with minimal wear, even under demanding circumstances. This compliance not only promotes machine longevity but also contributes significantly to workplace safety and productivity.
In conclusion, understanding the necessity of centrifuge balancing cannot be undervalued. It is not merely an optional maintenance task but an essential component of operational efficiency in any industry relying on these machines. By overlooking the importance of regular balancing practices, industries inevitably face prolonged wear, diminished productivity, and heightened risks of catastrophic machinery failure. The use of modern devices, such as the Balanset-1A, plays a critical role in ensuring that centrifuges operate safely and efficiently. Ultimately, the investment in dynamic balancing pays dividends by minimizing repair costs and reducing production downtimes, paving the way for sustained industrial success.